COMET_COHERENCE - Evolution of the coherence for the comet graph
Description
This package contains the code to reproduce all the figures of the paper:
Global and Local Uncertainty Principles for Signals on Graphs
Authors: Nathanael Perraudin, Benjamin Ricaud, David I Shuman, Pierre Vandergheynst
Abstract of the paper
Uncertainty principles such as Heisenberg's provide limits on the time-frequency concentration of a signal, and constitute an important theoretical tool for designing and evaluating linear signal transforms. Generalizations of such principles to the graph setting can inform dictionary design for graph signals, lead to algorithms for reconstructing missing information from graph signals via sparse representations, and yield new graph analysis tools. While previous work has focused on generalizing notions of spreads of a graph signal in the vertex and graph spectral domains, our approach is to generalize the methods of Lieb in order to develop uncertainty principles that provide limits on the concentration of the analysis coefficients of any graph signal under a dictionary transform whose atoms are jointly localized in the vertex and graph spectral domains. One challenge we highlight is that due to the inhomogeneity of the underlying graph data domain, the local structure in a single small region of the graph can drastically affect the uncertainty bounds for signals concentrated in different regions of the graph, limiting the information provided by global uncertainty principles. Accordingly, we suggest a new way to incorporate a notion of locality, and develop local uncertainty principles that bound the concentration of the analysis coefficients of each atom of a localized graph spectral filter frame in terms of quantities that depend on the local structure of the graph around the center vertex of the given atom. Finally, we demonstrate how our proposed local uncertainty measures can improve the random sampling of graph signals.
This experiment
In this example with investigate the Fourier coherence of comet graphs. They are composed of a star with \(k\) vertices connected to a center vertex, and a single branch of length greater than one extending from one neighbor of the center vertex (see Figure~1). If we fix the length of the longer branch (it has length 10 in Figure 1), and increase \(k\), the number of neighbors of the center vertex, the graph Laplacian eigenvector associated with the largest eigenvalue approaches a Kronecker delta centered at the center vertex of the star. In this configuration, some of the Laplacian eigenvectors become more concentrated as the number of branches of the star increases, with a shape tending to a Kronecker delta. As a consequence, the coherence between the graph Fourier and the canonical bases approaches 1 as \(k\) increases.
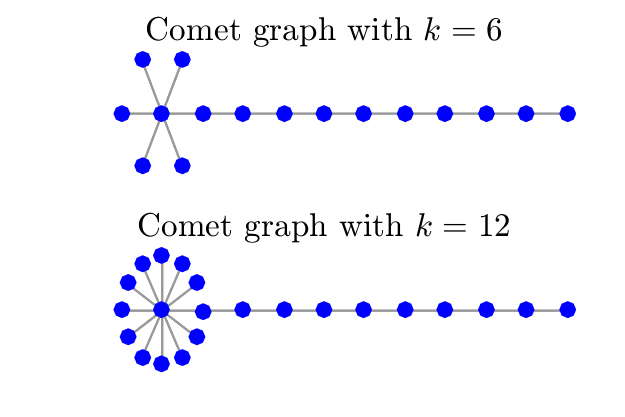
Two different star graphs
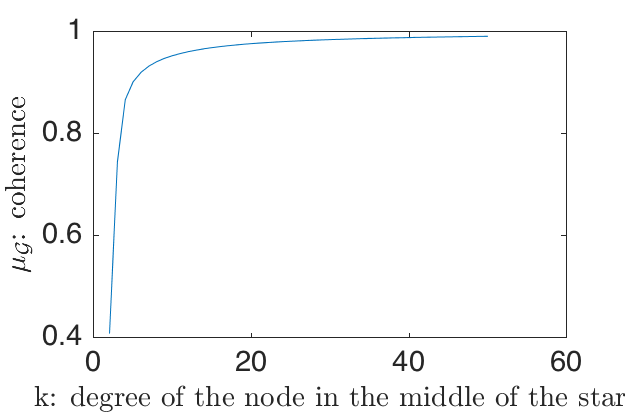
Coherence
References:
N. Perraudin, R. Benjamin, S. David I, and P. Vandergheynst. Global and local uncertainty principles for signals on graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.03030, 2016.